All About Indian Spices
Delivery
Online Shop
Discounts
Easy Pay
Security
Indian Spices Online
-
Sale!

8MM Cardamom
MRP From ₹610.00 Quick ViewBuy NowSelect options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

Biriyani Spice Pack
MRP Original price was: ₹949.00.₹749.00Current price is: ₹749.00. Quick ViewBuy NowAdd to cart -
Sale!

Brindleberry / Cambodge
MRP From ₹259.00 Quick ViewBuy NowSelect options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

Ceylon Cinnamon Powder
MRP Original price was: ₹369.00.₹349.00Current price is: ₹349.00. Quick ViewBuy NowAdd to cart -
Sale!

Ceylon Cinnamon Powder 180g
MRP Original price was: ₹520.00.₹499.00Current price is: ₹499.00. Quick ViewBuy NowAdd to cart -

Coriander
MRP From ₹99.00 Quick ViewBuy NowSelect options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Sale!

Coriander Powder 180g
MRP Original price was: ₹260.00.₹249.00Current price is: ₹249.00. Quick ViewBuy NowAdd to cart -
Sale!

Cumin Powder 180g
MRP Original price was: ₹221.00.₹199.00Current price is: ₹199.00. Quick ViewBuy NowAdd to cart
Why is India called the Spice Capital of the World?
India produces about 2.5 million tonnes of spices every year. Out of which around 200,000 tonnes are exported to other countries. Indian spices are popular throughout the world for their unique flavour, vibrant colours, and heavenly aroma. The climate conditions in several parts of India are perfect for growing and cultivating different spices. High rainfall, heavy humidity, dry and hot weather climates are ideal for growing spices spread throughout different parts of the country.
Indian spices are widely used for their medicinal, seasoning, and preservative effects. The flavour profile in the typical Indian households consists of turmeric, black pepper, clove, red chilli, coriander, cinnamon, etc which holds a staple and important position in Indian cuisine. Spices like ginger, fenugreek, and turmeric have been used as medicines since ancient times. Spices like cloves, cardamom, etc also act as mouth refreshing agents.
Spices are at the very heart of Indian cuisine. Spices are not just found in the everyday Indian kitchens but they have huge cultural and religious implications in a country such as India. They are mentioned in the ancient Hindu scriptures known as the Vedas, the Old Testament, and ancient Egyptian papyruses. They are also believed to have healing and magical qualities in several Indian cultures. They have also been used to embalm corpses, cast spells, incenses in religious rituals, and as aphrodisiacs. It was not until the Roman conquests the Western countries discovered their culinary possibilities. In their long and tumultuous history, spices have often been more valuable than jewels, gold, or other precious stones. The trade of spices has been an extraordinarily influential factor in several wars and trade throughout history.
The simplest of natural ingredients such as flower, leaves, roots, seeds, bark, and bulbs are used in a variety of combinations of flavours: hot, spicy, sweet, sharp, mild, sour, fragrant, or pungent. All these different flavours and aromas combine to create an explosion of flavours on your plate. Hot spices are generally used in most styles of Indian cooking and it is also the most coveted group of spices among the various groups of spices by the West. Researchers have suggested that the burning sensation while consuming hot spices is the pain of nerve endings on the tongue. This leads to the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers giving rise to pleasurable and even euphoric sensations in your mouth.
Where are spices grown in India?
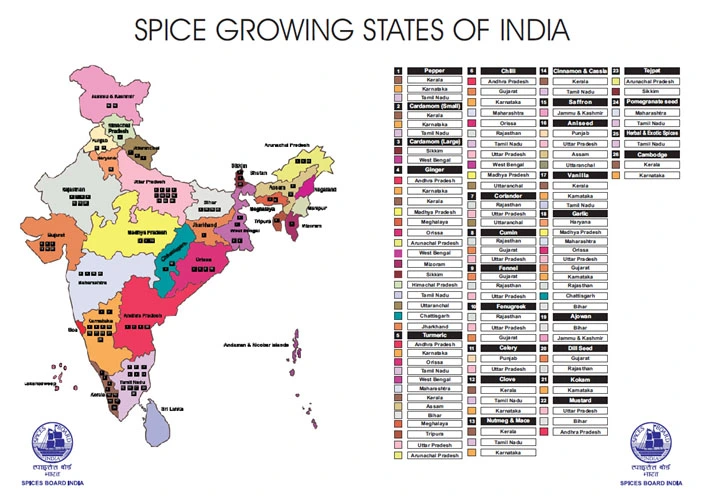
India is home to a wide variety of spices that are used for its culinary and medicinal values. Some of the most popular spices grown in India are Pepper, Chilli, Cinnamon, Saffron, Coriander, Aniseed, Fenugreek, etc. India is a diverse country with a variety of geographical and climatic conditions. Therefore several spices are grown in different states where the weather, climate, soil, etc is appropriate for its growth.
Pepper is mainly grown in the southern states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. Small cardamom is also mainly grown in southern states such as Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. Large cardamom on the other hand is mainly grown in two states, West Bengal and Sikkim.
Ginger is produced in several states such as Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Arunachal Pradesh, Orissa, Meghalaya, West Bengal, Mizoram, Sikkim, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Uttaranchal, Chattisgarh, and Jharkhand.
Turmeric is also produced in numerous states across India such as Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Orissa, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Kerala, Assam, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Chilly is produced in northern and southern states such as Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Orissa, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Uttaranchal. Coriander is mainly grown in states such as Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttaranchal.
Cumin is grown in Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Gujarat. Fennel and Fenugreek are also mainly grown in these three states.
Celery, another spice that India is famous for is grown in Punjab and Uttar Pradesh. Nutmeg & Mace along with Clove is mainly grown in three southern states. Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu are the main producers of these spices.
Cinnamon & Cassia are mainly grown in Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Saffron is one spice that is only grown in Jammu & Kashmir. Aniseed is grown in states such as Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, and Uttaranchal.
Vanilla is also another spice that is exclusively grown in the southern states such as Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. Dill seeds are grown in Rajasthan and Gujarat. Kokam is grown exclusively in Karnataka. Mustard is mainly cultivated in Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh.
Garlic is another spice that is cultivated in several states such as Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Bihar.
Tejpat is grown in Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim. Pomegranate seed is grown in Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu. Cambodge is mainly grown in the southern states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
What are the various spices grown in India?
India is a great exporter of spices. There has been a steady increase in area and production of spices in India. The annual growth rate in production and area is estimated to be about 5.6% and 5.6% respectively. Indian is known for its signature spices such as
Black Pepper
Black Pepper, “the king of spices” is the most cash earning crop among the many spices that India exports to other countries. Considered as one of the supreme peppers in the world, these berries are grown in the Piper nigrum trees found in the Western Ghats of Kerala. It is popularly used as a source of flavoring in several cooking styles all over the world.
Black Pepper is a tropical plant that grows as a vine and needs the support of the other trees in the ecosystem for its growth. It requires a minimum of 10° and a maximum of 30°C consistent temperature. Adequate and well-distributed rainfall ranging from 200-300 cm also helps promote its growth. It thrives on well-drained loamy soils, overlaying the hill tops of the Western Ghats. It can also be grown on red and laterite soils with careful planning and favorable conditions. It can also grow from almost sea level to an altitude of 1,200m.
India is the second-largest producer of black pepper after Indonesia. Its distribution is highly concentrated in the southern states such as Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. Even though it is produced in almost all districts of Kerala, the largest producer of Black peppers comes from the Kannur, Idukki and Wayanad districts followed by the other states.
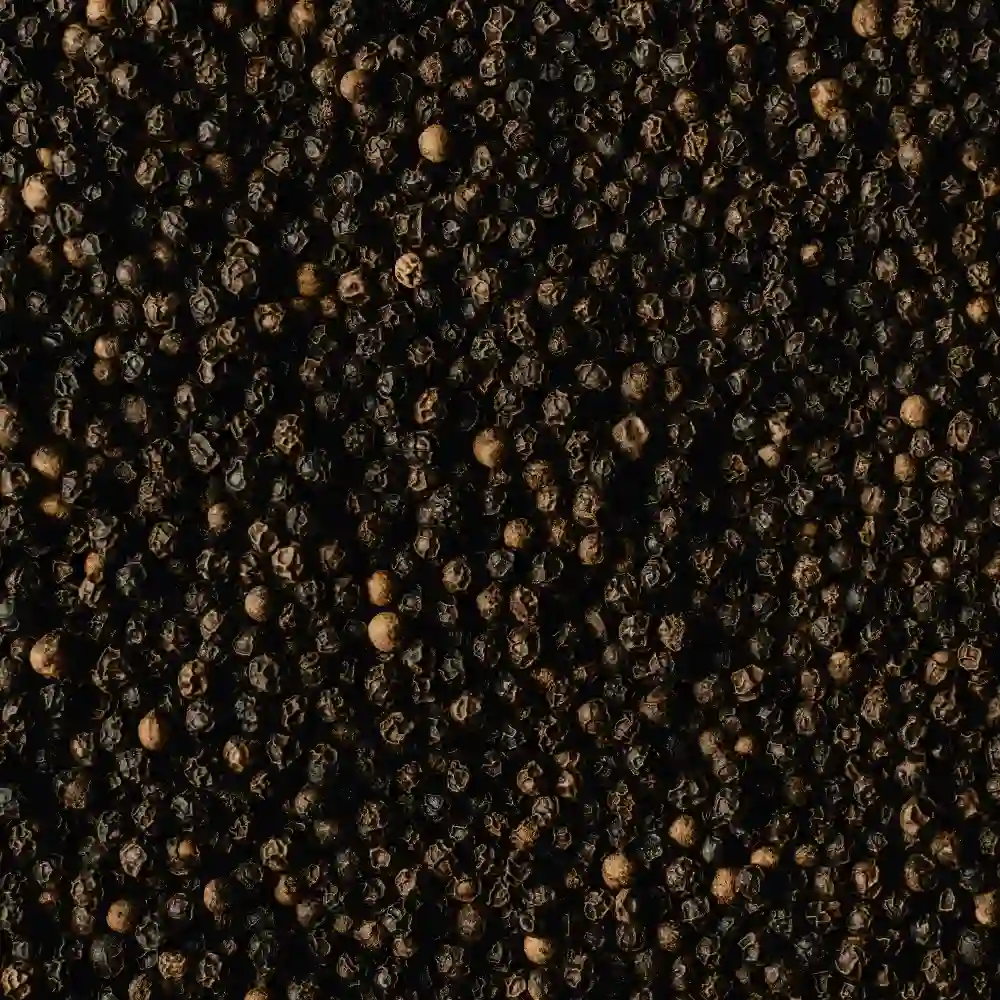

Karnataka is a distant second and only contributes around 3% of the total production in India. Tamil Nadu is also responsible for producing a small quantity of peppers. About one-third of the total production of black pepper in India is exported to foreign markets. India exports black pepper to around 80 countries in the world.
Black Pepper has a sharp and pungent aroma while maintaining a spicy and warm flavor. It is coated onto meats, teas, sauces, spice blends, etc to add depth to their taste. Black Pepper contains a variety of nutrients such as flavonoids, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and carotene which protects against several diseases.
Cardamom
Cardamom is known as the “queen of the aromatic spices” and is mainly used for flavouring dishes in various cooking styles and medicine. Green Cardamom is used as a key ingredient in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisines for savory recipes.
It grows optimally in high heat and humid conditions with temperatures ranging from 15°C and 32°C. It also requires a fairly distributed annual rainfall of 150-300 cm. Deep red and laterite soils with plenty of leaf mold and well-drained forest loams are the ideal soils suited for its consistent growth. Tropical rain forests with an altitude of 100-1600 meters above sea level are the best environment for its sustained growth. It is a shade loving plant and is therefore grown under shady trees.
India produces about 90% of the world’s total production of cardamom. Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu account for 53, 42, and 5 percent of the total production of Cardamom in India. In Kerala, the crop is largely grown in Idukki, Palakkad, Kozhikode, and Kannur. Madurai is the leading producer of Cardamom in Tamil Nadu and Kodagu, Chikmagalur, Hassan, etc are the leading producers in Karnataka. About half of the production of India is exported to around 60 countries in the world. India was relegated to the second position in total production and export of cardamom by Guatemala who accelerated the production from the mid-1980s. India needs to promote and boost its own production to overtake Guatemala shortly.
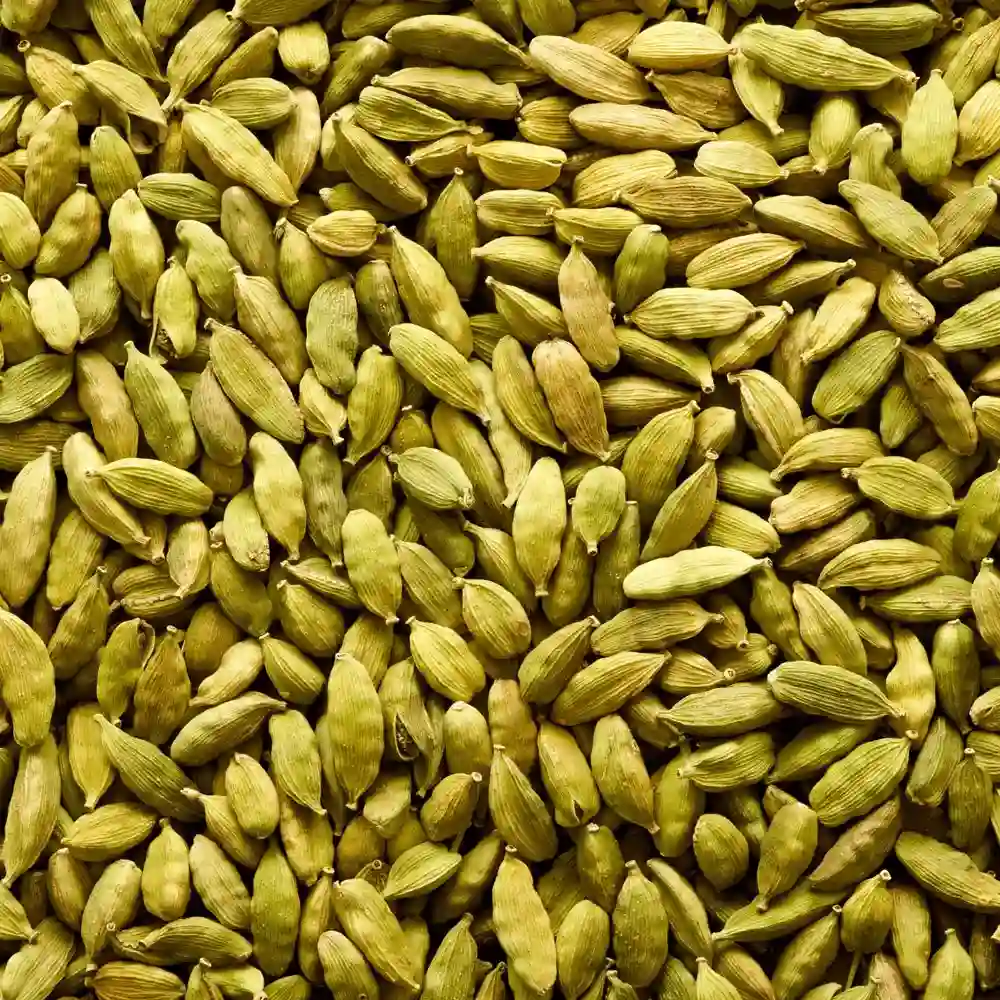

Green cardamom has an aromatic and piney aroma while comprising a spicy and minty flavor. It is added onto items such as pastries, puddings, poultry dishes, and beverages like tea and coffee to add depth to its flavor and to make the most of its medicinal properties. Cardamom contains various nutrients that help indigestion. It is mixed with other spices to gain relief from stomach issues such as nausea and vomiting.
Chillies
Chill powder is a red coloured blend of powdered spices such as cumin, garlic powder, cayenne, oregano, and paprika. Chilli powder is mild-moderately spicy depending on how much cayenne is blended onto it. Chillies are one of the most important spices produced in India.
The growth of chillies requires temperature ranging from 10° to 30°C and annual moderate rainfall of at least 60 cm to 125 cm. Extremely scarce or an abundance of rainfall is harmful to the crop. It can be cultivated on a variety of soils including black cotton soil and different varieties of loamy soils. It can be grown up to elevated plains of 1,700 meters.
Andhra Pradesh and Telangana are the biggest producers of chilli with districts such as East and West Godavari, Khammam, Guntur, Warangal, and Prakasam playing a major part in the production of chilli. Maharashtra and Orissa come a distant second in the production of chilli throughout the country. Other states such as West Bengal, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh also contribute to the total production of chilli in the country. The widespread use of chilli in Indian households means that only 5 to 7 percent are exported to countries such as the USA, Russia, and Sri Lanka while most of it is consumed within the country itself.
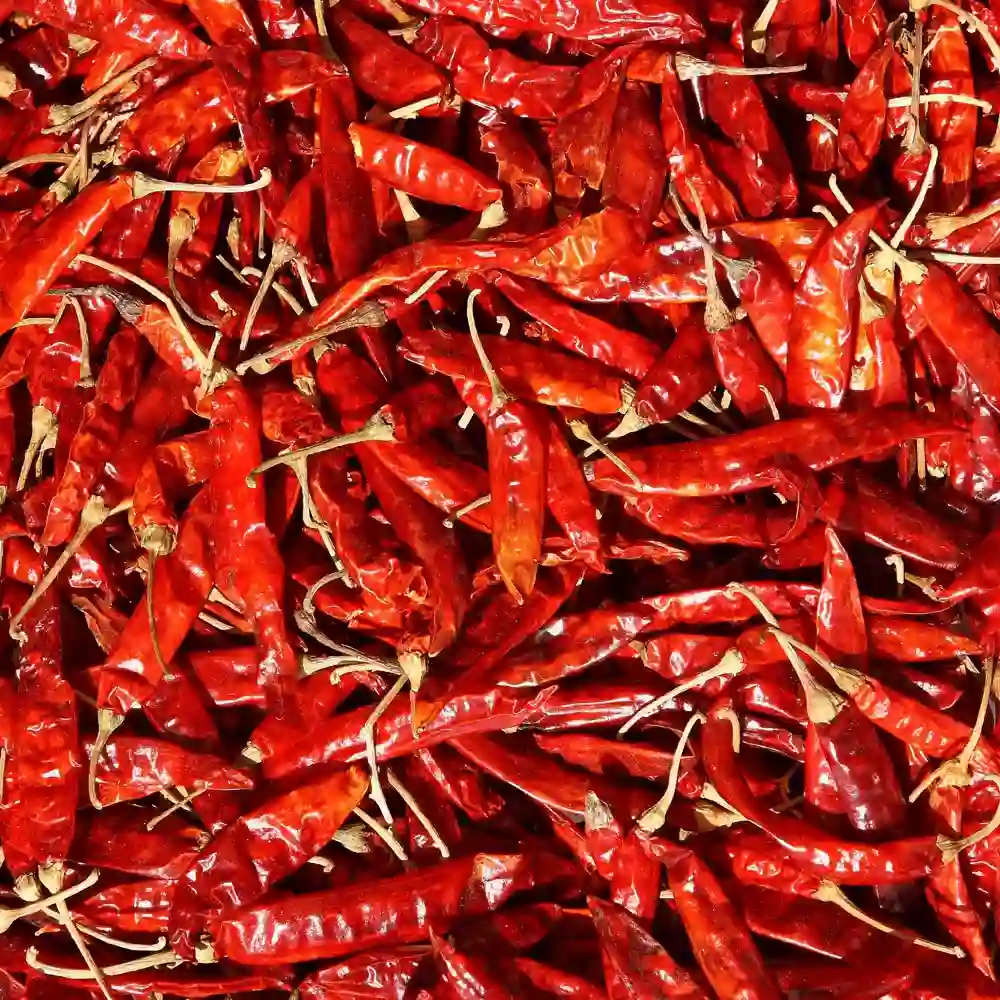

Chilli powder is used in various styles of cooking in different cuisines around the world. It is added to sauces, curries, meat preparations, soups, etc. Chill powder fights inflammation, promotes digestive health, cognitive functioning, nasal congestion, and aids in weight loss.
Ginger
Ginger is one of the most ancient spices known to man. It is grown from Zingiber officinale trees found in the Western Ghats of Kerala. Ginger is one of the most vital spices used throughout the world in various cultures around the world. ginger is derived from a rhizome and grows underground bearing both roots and shoots. It is available mainly as fresh and dried.
India is the largest producer of ginger in the world producing about 80 percent of the total production. It is mainly grown in tropical and sub-tropical climates and requires consistent temperatures ranging from 10° to 25 °C temperature. They also require 125-250 cm annual rainfall for optimal growth. Well-drained sandy, clayey or red laterites, and loams are the most ideal soils for its cultivation. It can also grow above sea level to an altitude of 1,300 m.
Kerala, Meghalaya, Sikkim, Orissa, Mizoram, and West Bengal are the main producing states and account for nearly 84 percent of the total production of the country. Kerala is the largest producer. About 80 percent of our exports go to the West Asian countries. India is a major exporter of ginger in the international market and accounts for about half of the world’s total trade. 80 percent of the ginger exported from India goes to West Asian countries. 80 to 90 percent of the total production of ginger produced in the country is consumed within the country as it is a staple throughout Indian cuisine.
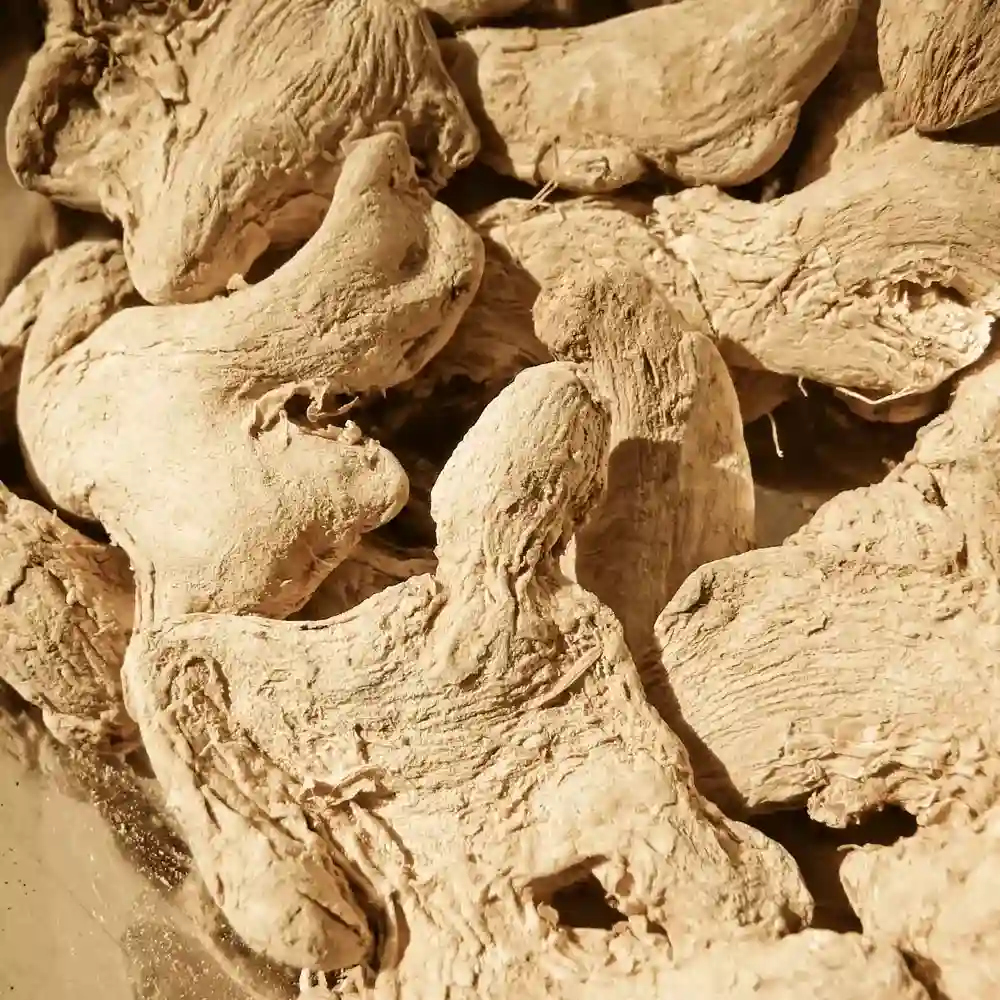

Ginger has an aromatic and fresh aroma while comprising of a pungent and zingy flavor. Dried ginger is used as a key ingredient in the culinary world for the crafting and preparation of various dishes. It is used in both sweet and savory items such as curries, sauces, biscuits, bread, and meat dishes. It is also mixed into beverages such as beer, ale, wine, and tea to add its unique flavor and make the most of its medicinal benefits. Ginger is host to several compounds which is found to be important in combating several diseases. Ginger has also been used for centuries to treat digestion as it contains phenolic compounds which are known to help relieve gastrointestinally (GI) irritation, stimulate saliva and bile production, and suppress gastric contractions.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a golden-colored spice that is used in various applications around the world. It is used as a pivotal ingredient in several cuisines and is also used as a form of dye for clothing and threads in the textile industry. Turmeric is the native of the tropical lands of South-East Asia. Turmeric is one of nature’s most vibrant spices.
Turmeric requires a tropical climate and well-drained sandy and clayey loams, medium black, red, or alluvial soils for its growth. India is one of the major producers of turmeric in the world. Andhra Pradesh is the largest producer of turmeric, accounting for half of the total production of India. Guntur and Cuddapah districts contribute two-thirds of the state’s total production. Karnataka is the second-largest producer, producing about 20 percent of the total production of India. Mysore and Belgaum are outstanding producers, Third place is occupied by Tamil Nadu, which produced more than 10 percent of the turmeric of the country. Coimbatore accounts for around 60 percent of the state’s production. Other states such as West Bengal, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Bihar, Assam, and Tripura also contribute to turmeric production in the country. About 90 percent of the total production is consumed within the country and the remaining 10 percent is exported to countries such as the USA, Japan, Russia, Singapore, and Sri Lanka.
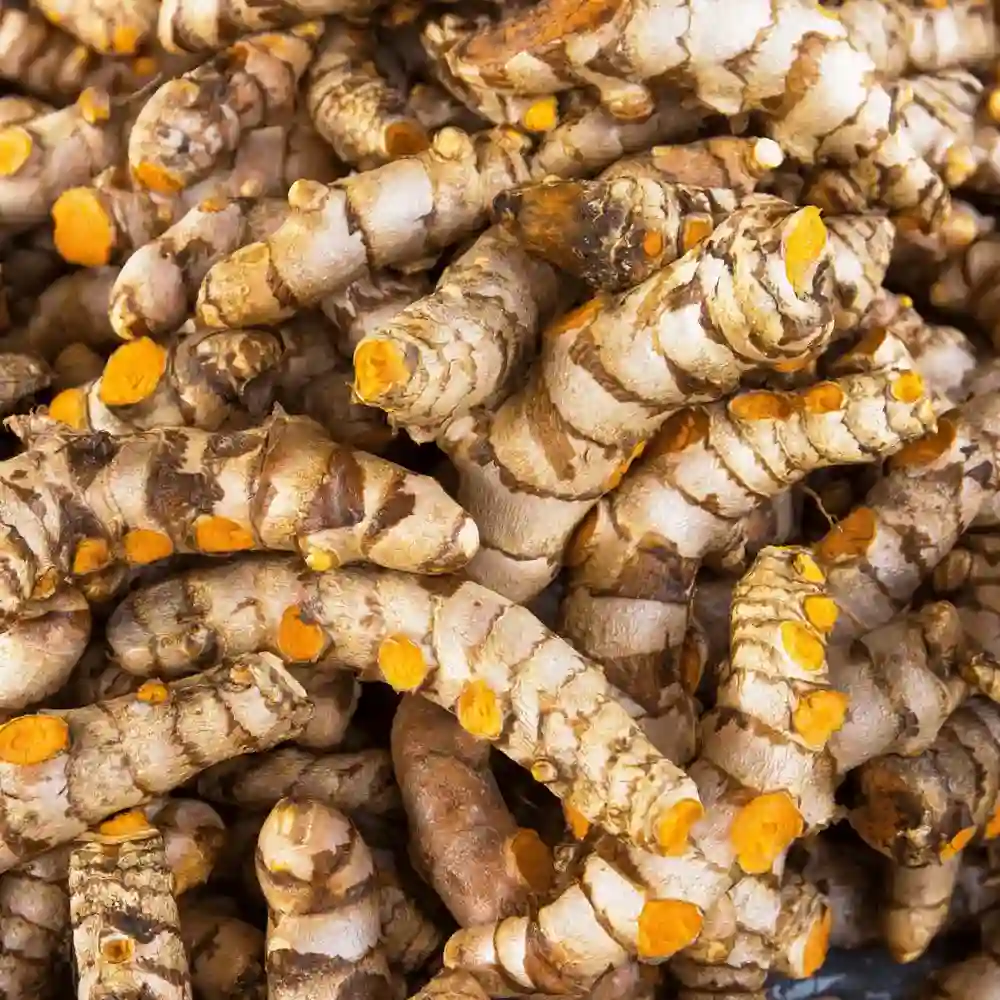

Turmeric has an earthy and musky aroma while comprising of a sour and slightly bitter flavor. Turmeric plays a pivotal role in the Indian style of curry cooking as it is an essential ingredient to most masalas and curry powders. It has also become a staple for soups, risottos, cakes, pickles, and cheese. It is also added to several nonalcoholic beverages such as tea, lemon water, and tonics to add a dose of spiciness. It is also exclusive to the food industry and the clothing industry for its coloring properties. Turmeric is also a sign of prosperity and fertility, therefore, is used in celebrating several religious ceremonies.
Turmeric is used as a mood stabilizer as the compound curcumin in turmeric boosts the brain-building protein BDNF and also secrete serotonin and dopamine-two chemicals that impact happiness in the brain. Turmeric contains anti-inflammatory properties that help fight obesity by regulating the growth of fat cells. Turmeric also promotes heart health its anti-inflammatory properties prevent heart diseases and heart attacks.
Cloves
Cloves are the most well-known spice in the group of spices known as “flower spices,”. The tree from which Cloves are harvested has the scientific classification “Syzygium aromaticum” and is indigenous to the Moluccas in Indonesia. Its rise was propagated due to the natives who planted a clove tree for each child born. Cloves are propagated through seeds during the summer months of June-October. Cloves are used in various forms all over the world.
Cloves can be cultivated across most parts of the country but it is mainly cultivated in the hilly tracts of the Western Ghats and red soils of Kerala and Tamil Nadu due to its ideal weather conditions. Cloves thrive best in a warm humid tropical climate with annual rainfall ranging from 150 to 250 cm. It also grows well when it is above sea level up to an altitude of 800-900 meters. Clove plants also grow optimally in partly shady regions. Cloves grow ideally in rich loamy soils in wet tropical areas. Cloves can also grow in heavier red soils but in both cases, they require good drainage for better quality and yield. Tamil Nadu is the largest clove producing state in the country with a contribution of around 78% of the total production in India. Karnataka is a distant second with around 14% of total clove production happening there. Kerala accounts for almost 6% of the total production of cloves in the country. Other states also produce small quantities of cloves which account for around 1% of the total production in India.
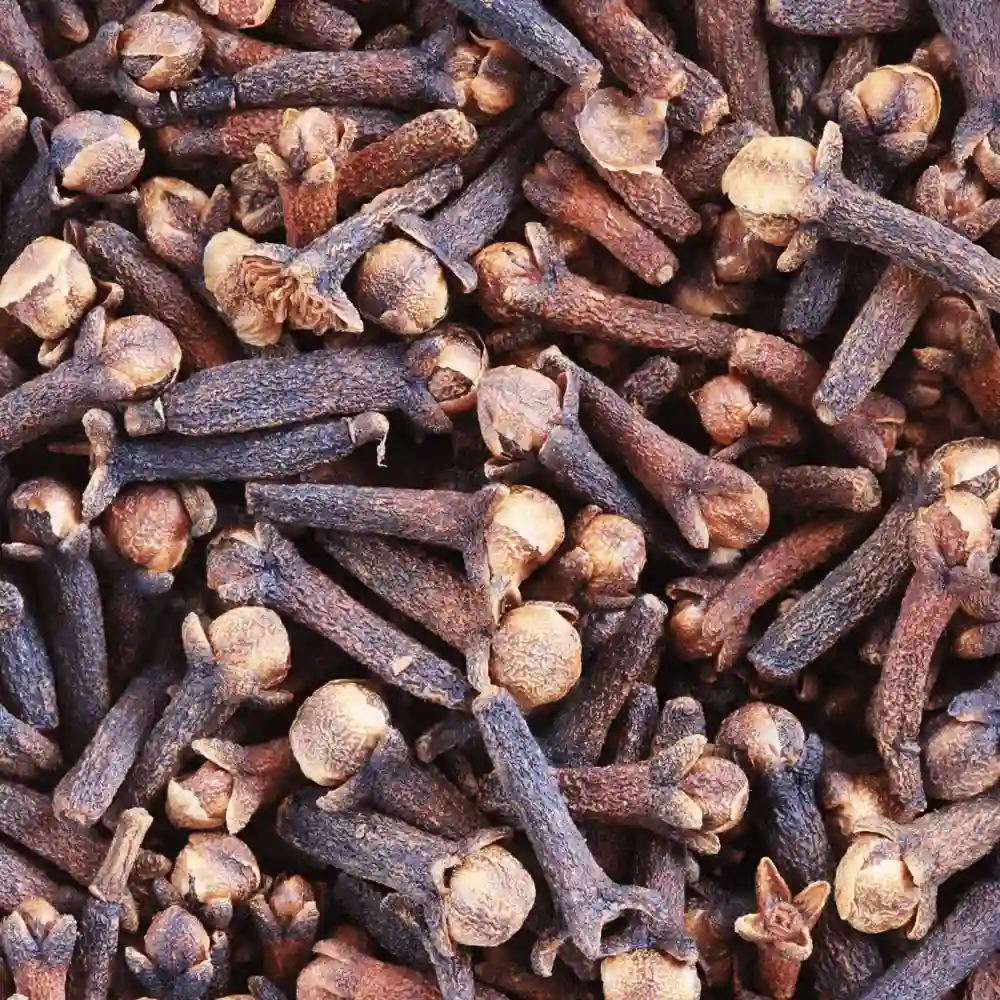

Cloves have a warm and pungent aroma while maintaining a strong sweet flavor. It is also an excellent flavoring agent for savory dishes as well. Cloves are used in various forms all over the world. They are mainly used for culinary purposes. Their sweet flavor is used to enhance food items such as sweets, cakes, cookies, and add depth to items such as sauces and soups. Cloves contain a variety of nutrients such as Fiber, Vitamin K, Vitamin C, manganese and Vitamin E. Cloves are an effective tool in improving digestive health as they secrete digestive enzymes that eliminate bloating and indigestion.
Fenugreek
Fenugreek is a spice that is used worldwide for its culinary and medicinal benefits. The fenugreek is produced for its leaves and seeds which are used as a herb or spice respectively. It is available as whole and powdered.
It has wide adaptability and is successfully cultivated both in the tropics as well as temperate regions. It is tolerant of frost and freezing weather. It does well in places receiving moderate or low rainfall areas but not in heavy rainfall areas. It can be grown on a wide variety of soils but clayey loam is relatively better. The optimum soil pH should be 6.0 to 7.0 for its better growth and development.
Fenugreek is a versatile spice that can be successfully cultivated in most regions. It grows well in tropical as well as temperate regions. It can endure and continue its growth in frost and freezing weather conditions. It also grows optimally in regions receiving low or moderate rainfall but fails to grow suitably in areas with heavy rainfall. It can grow in a wide variety of soils but clayey loam is the ideal type of soil for its growth. The soil PH should be around 6.0 to 7.0 for its better growth and development. India is one of the major fenugreek producing countries in the world. Rajasthan accounts for more than 80% of the fenugreek production in the country. Other states such as Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and Gujarat are also involved in the production of fenugreek. It is exported to other major countries such as the UK, Japan, Korea, Saudi Arabia, and Sri Lanka.
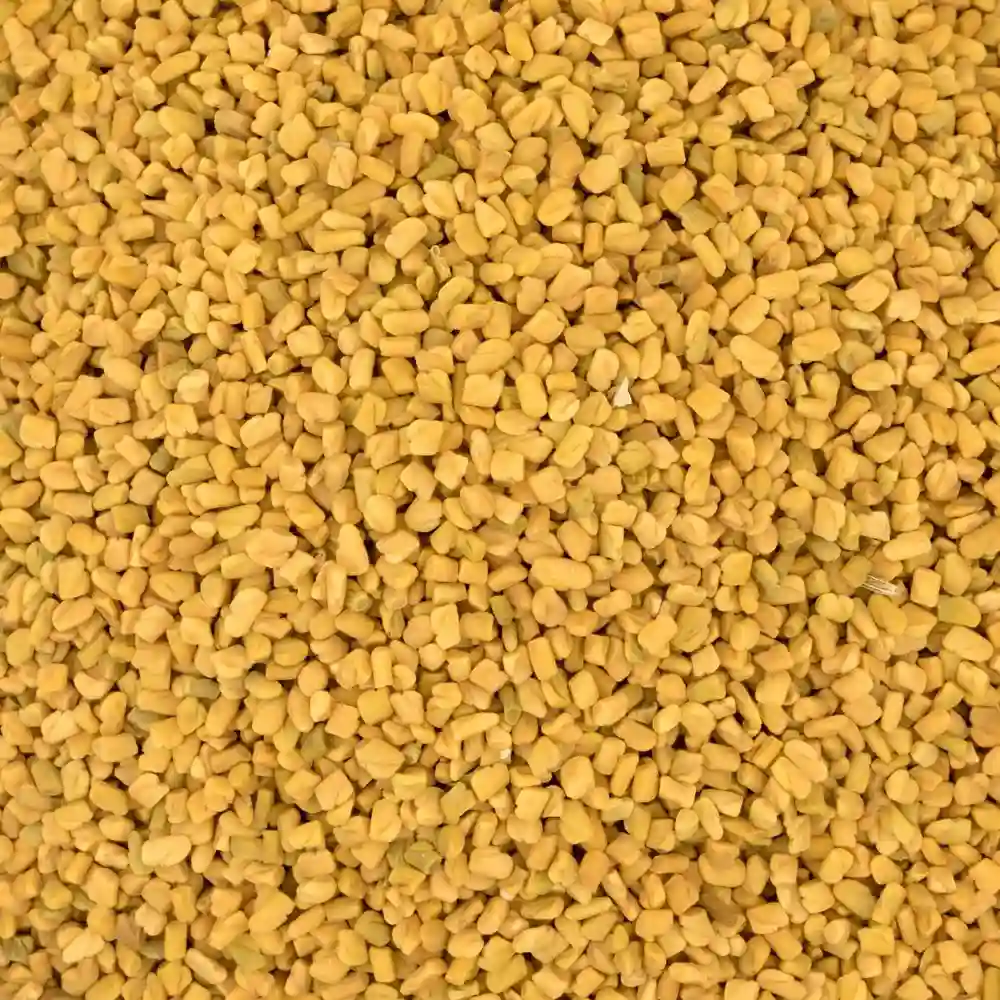

Fenugreek has a musky and fresh aroma while comprising of a strong and bitter flavor. Fenugreek is popular in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisines. It is used as a primary ingredient in curry powders and is added to items such as pickles, dals, soups, sweetbreads, and potato dishes. t is also mixed into drinks such as water and tea to make use of its medicinal benefits. Fenugreek is host to several supplements which is found to be important in fighting and preventing several diseases. It has been used in alternative medicine and Chinese medicines dating back centuries in treating skin diseases.
Corriander
Coriander is an important spice used throughout the world for its flavoring properties. The whole of the coriander plant is edible but it is mainly produced for its fruits and its tender green leaves. It plays a pivotal role in flavoring various types of dishes and holds a prime position in the culinary world. Coriander is one of the sweeter spices that exist today which is strange because the leaf of the coriander plant which is known as cilantro is spicy.
Well-drained loamy soils are the ideal soil for its growth. It grows optimally at a temperature range of 20-25°C. Climatic conditions should ideally be consistently cool and dry. A frost-free climate is key for the exponential growth of coriander. Approximately 80% of the world’s coriander is produced in India. India is the largest producer, consumer, and exporter of Coriander. Rajasthan is responsible for 80% of the country’s total coriander production. Other states such as Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu comprise the remaining 20% of the total production of coriander in India. The spice is an important item in international trade.
Coriander has a warm and floral aroma while comprising of an earthy and sweet flavor which is incorporated onto several cuisines to highlight the complexity of each dish.
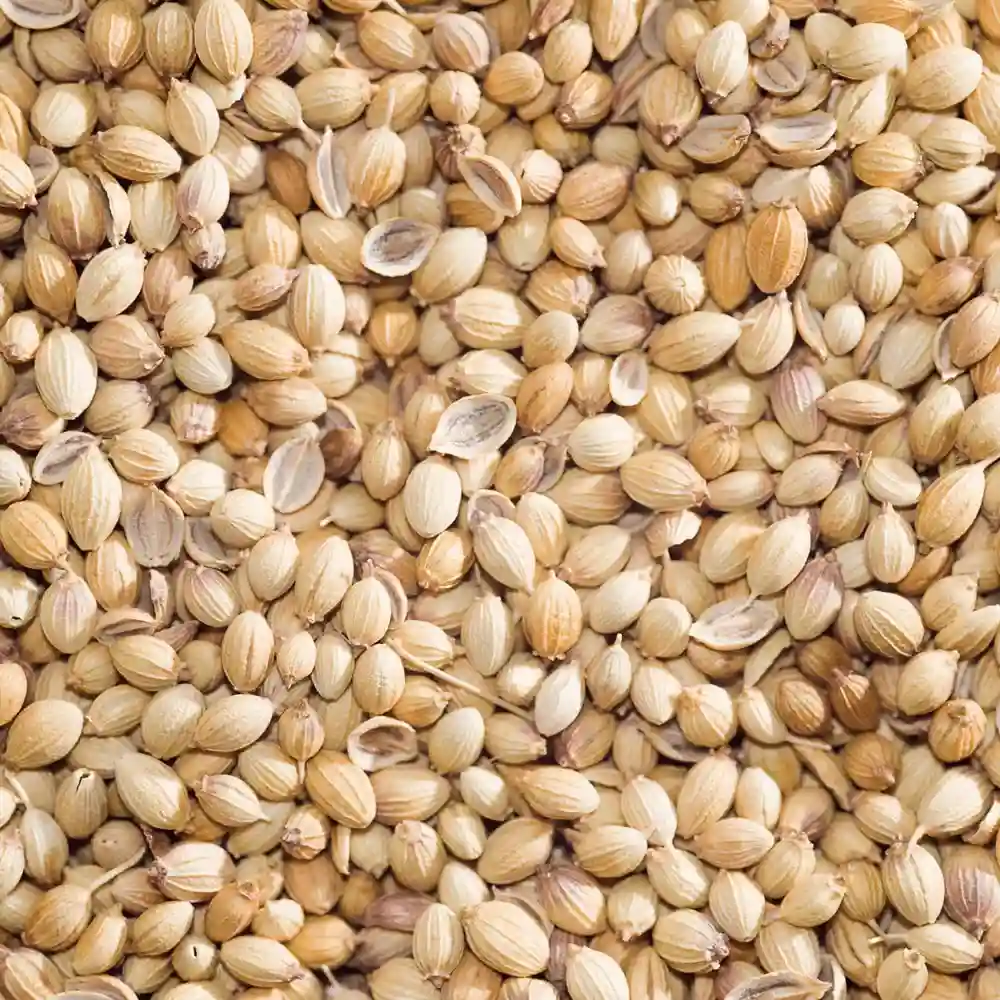

Coriander is used as a key ingredient in the European and Asian styles of cooking. It is added to items such as soups, stews, pickling spices, and poultry dishes. It is also an important mixture in the brewery industry as it is used actively for its complex flavoring. It is also combined into tonics for its medicinal properties. Coriander is one of the oldest spices in the world as its use has been recorded during the times of the Ancient Egyptians as well as being mentioned in the Holy Bible. Green cardamom contains several compounds that are found to be important in the prevention and curing of several diseases.
Arecanut
Arecanut is a hard nut that is cut into small pieces from the Areca tree, a tropical tree. Its stem is used for construction purposes and leaves for thatching. It has commercial and economic importance not only in India but also in Southeast Asia and China. India is the largest producer of areca nut in the world.
Its cultivation can be done from sea level to 1,000 meters. It thrives inland having 15° to 35°C temperature and 200-300 cm annual rainfall. It grows on a variety of soils such as well-drained laterite, alluvial soils to red loamy soils. Arecanut can be cultivated from sea level to about 1,000 meters.
Some of the largest producing states of areca nut are Kerala, Karnataka, Assam, Tripura, and Meghalaya. They account for around 90 percent of the total production of areca nut in India. Kerala is the largest producer accounting for 37 percent of the Indian production. Districts such as Malappuram, Kannur, Kollam, Kozhikode, and Thrissur are the main producers of areca nut in Kerala. In Karnataka, it is mainly grown in Dakshina Kannada, Chickmagalur, Uttar Kannada, Shimoga, and Tumkur districts.
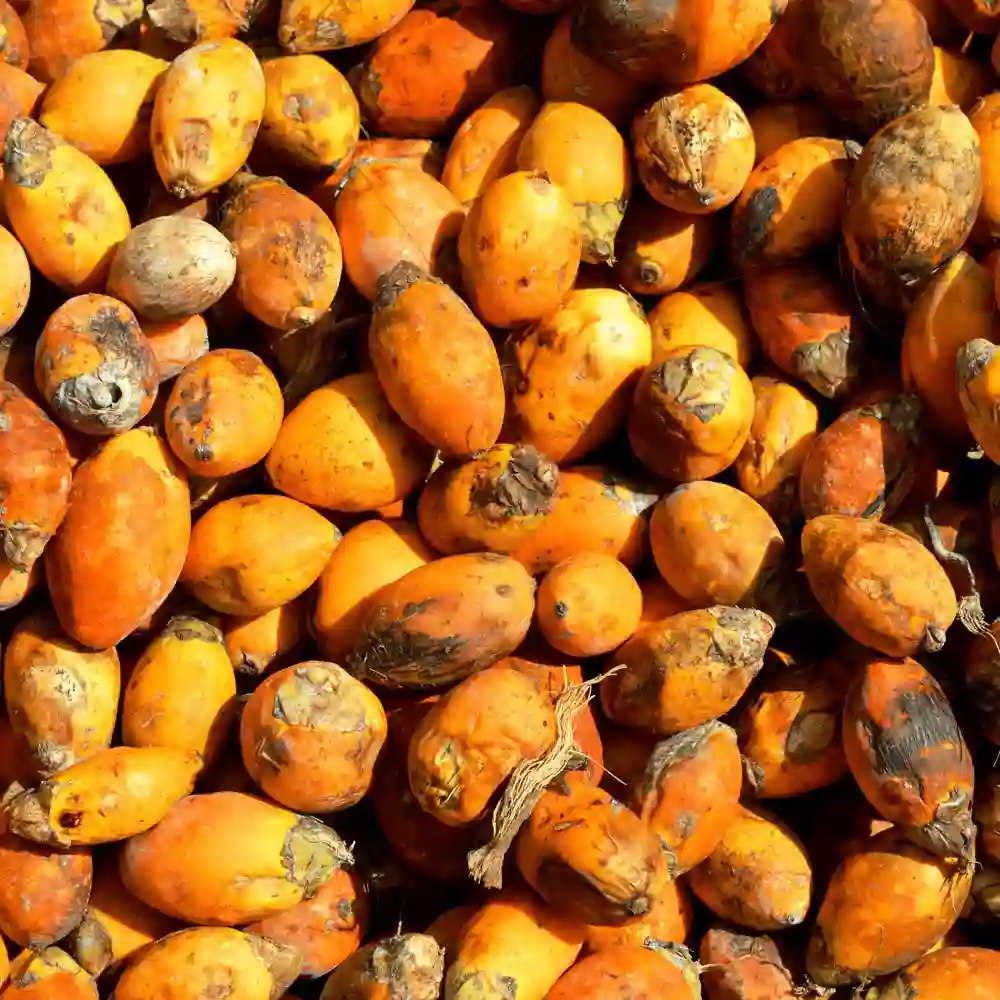

Assam produces about one-fourth of India s areca nut where Kamrup, Sibsagar, and Darrang districts are important producers. Ratnagiri and Kolaba districts of Maharashtra, Coimbatore, and Salem districts of Tamil Nadu are other important producers. West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Goa, and Pondicherry also produce some areca nut. Assam produces about one-fourth of India’s areca nut where Darrang, Sibsagar, and Kamrup are important producers. Ratnagiri and Kolaba districts of Maharashtra, Coimbatore, and Salem districts of Tamil Nadu are the other important producers of Arecanut. Other states such as West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh also produce areca nut in smaller quantities.
Most of the areca nut produced in the country is consumed within the country itself especially in the South Indian states while a small quantity is exported mainly to Nepal, UAE, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Kenya, and Singapore. Areca nut and the plant as a whole is used widely in India and South Asia as a stimulant for chewing purposes, medicine, timber, fuelwood, clothing, lubricant, vegetable, etc. The nut is chewed with the betel leaf as it has a stimulating effect.
What is the history of the Indian spice trade?
Buying spices such as cinnamon, black pepper, cardamom, cloves, etc are relatively cheap that it is hard to believe that they were as valuable as gold and silver in the past. The coming of the Portuguese in Calicut, India changed the course of world history and opened up the trade of spices to different countries in the world.
In 1498, Vasco Da Gama landed on the shores of Calicut, India by discovering an alternative route that helped assert control of the spice industry by the Portuguese. Under the impetus of the spice trade, Portugal expanded territorially and commercially through the momentum of the spice trade. By 1511, the Portugese had a monopoly over the spice trade of the Malabar coast of India and Ceylon. In the 16th century over half of Portugual’s revenue came from West African gold and Indian spices namely pepper. Portugal slowly started losing their rein of control in the 1590s after stiff competition from pepper growers and the successful attack of the Dutch.
With Portugal slowly losing their monopoly in the spice trade, the English and the Dutch capitalized to gain control over the spice trade. Dutch explorers made friends with native sultans and organized trading posts which gave the Dutch control over the spice trade in the 17th century. England’s immense foothold over the sea saw them slowly acquire spice cargoes and finally in 1780 England and Holland were at odds with each other which severely weakened Dutch resources. By the 1800s the British controlled everything that was once controlled by the Portuguese and the Dutch.
How do you select the best quality Indian spices?
Selecting the best quality Indian spices is crucial for enhancing the flavour and health benefits of each meal you prepare in the kitchen. There are four key metrics to keep in mind when selecting high-quality Indian spices. They are
Picking the right region: Some spices are exclusively cultivated in different parts of the country. It is important to ensure that the spices you pick to purchase are sourced from the very best regions appropriate to the growth of the spice. A little bit of research into the point of origin of the spice will greatly benefit your culinary experiences and enhance the quality of the food you consume.
Picking the right farm: It is important to make sure that the spices that you buy online or from your favourite retailer are sourced from the very best farms in the country. It is important to research the farming conditions and the cleaning processes the spice undergoes before it is sold for consumption.
Picking the best plant variety: It is important to determine what plant variety is most suitable for your purpose be it medicinal, culinary, or artistic. The spice or plant can be used for many different things and it is up to you to research and determine which plant variety is most suitable to achieve your goal.

Picking the best processing method: It is important to determine which farms use the most appropriate cleaning and processing method after the cultivation of the spices. The quality of the spices is thoroughly refined after cultivation depending on the cleaning and processing method used. Hence it is important to study what methods work best for a specific spice and making sure that it is being adhered to in the farming process before buying.
Conclusion
It is important to gain knowledge on spices through its history, origin, areas of cultivation, etc as it is used every day in your kitchens. It is important to make sure that the ingredients that you cook with are of the highest quality and come from authentic farms throughout the country. It is important to understand where each spice is grown optimally and whether the ingredients you buy are sourced from well-maintained farms. It is also important to understand which plant varieties are to be used for the task at hand. In this day and age demand is met with supply at all times but it is important to ensure that the spices you buy are picked from the right region, sourced from the best farms, and processed through scientifically approved methods for the best yield. Fortunately, we comply with all these conditions and make sure that the customer gets the best quality yield possible. The key is to unlock the door to an array of high-quality Indian spices that are packed with aroma and flavour intact. Thottam Farm Fresh is a trusted name in sourcing the nation’s high-quality spices and is perfectly sealed to ensure that these versatile spices reach your kitchen cupboard safe and healthy.
